Vol. 8 (2025), Article ID 246168, 10 pages
Research Article
Study of Dibutyltin(IV) Complex of Some Schiff Bases of Hydrazone Ligands and Their Effects as Antimicrobial, Antifungal, DFT Calculation, and Molecular Docking
Abeer Taha Ibrahim,1 Hatem Mohamed Shehata,1,2 Mohamed Refaat Shehata,1 Ahmed Abdo El-Sherif,1 and Laila H. Abdel-Rahman3
1Chemistry Department, Faculty of Science, Cairo University, 12613 Giza, Egypt
2El-Galaa Maternity Teaching Hospital, 11432 Cairo, Egypt
3Chemistry Department, Faculty of Science, Sohag University, 82534 Sohag, Egypt
Received 5 January 2024; Revised 27 May 2024; Accepted 19 June 2024; Published 13 June 2025
Abeer Taha Ibrahim, Hatem Mohamed Shehata, Mohamed Refaat Shehata, Ahmed Abdo El-Sherif, and Laila H. Abdel-Rahman, Study of dibutyltin(IV) complex of some Schiff bases of hydrazone ligands and their effects as antimicrobial, antifungal, DFT calculation, and molecular docking, Journal of Transition Metal Complexes, 8 (2025), art246168. doi:10.32371/jtmc/246168
The complex of dibutyltin(IV) dichloride with Schiff-base of hydrazone ligand has been synthesized and characterized. The complex formed was characterized by conductance measurements, elemental analysis, TGA, FTIR, and 1H NMR. DFT calculations have been achieved to study the equilibrium geometry of hydrazone ligand and its dibutyltin(IV) complex. The optimization of the dibutyltin(IV) complex structure shows that the Sn atom is six-coordinated in an octahedral geometry and the hydrazone ligand nitrogen atoms and the two chloride ions are in one plane. The distance between the two nitrogen atoms in the free hydrazone ligand is 2.944 Å and decreased to 2.647 Å in the complex. The anti-microbial activities of the ligand L and dibutyltin(IV) dichloride and [Sn(C4H9)2LCl] complex have been done against various strains of bacteria antimicrobial Staphylococcus aureus (+ve), Klebsiella pneumonia (-ve), Escherichia coli (-ve) and against antifungal Candida albicans. The complex exhibited higher activity against Gram-positive Staphylococcus aureus than Gram-negative Escherichia coli and Klebsiella pneumonia. The optimized most stable configurations of the ligand and [Sn(C4H9)2LCl] were obtained from the Gaussian 09 proGram. Molecular docking was performed using MOA2022 software on Staphylococcus aureus (Gram +ve bacteria) (PDB ID: 1jij) and antifungal Candida albicans.
dibutyltin(IV) complexes; hydrazone; Schiff-bases; biological studies, DFT, docking
The anticancer activity of coordination compounds, R2SnX2L s, is determined by the properties of the ligand.
The coordinated ligand (L) facilitates drug trafficking into cells in a certain fashion, but the organotin(IV) moiety that is separated from the complex is responsible for any anticancer action [1]. The latter would behave similarly to how the commonly used anticancer medication cisplatin interacts with nucleic acids. Consequently, there is a connection between the anticancer activity of the organotin(IV) compounds and their stability. This is combined with our earlier research on complexes of organotin(IV) [2,3,4,5,6,7,8,9,10,11,12,13].
Schiff-bases have shown various biological actions in biological chemistry, such as antibacterial, analgesic, anti-inflammatory, antiviral, antipyretic, antifungal, and antimalarial [14,15,16]. Due to their unique qualities and structural modifications, such as their thermal stability, versatility in coordination, biological and catalytic activities, and preparative accessibility, Schiff-bases are a noteworthy class of chemicals that have drawn significant interest across a wide range of domains [17,18,19,20,21].
In inorganic chemistry, heterocyclic hydrazone molecules are highly intriguing scaffolds. Many biological activities, including antifungal, anti-HIV, antibacterial, and antimicrobial properties, have been reported for them [22,23,24]. Schiff-bases are used as models for organisms known to exist in biology because of their high chelation affinity and suitability for solid metal complexes [25].
Hydrazones are an important class of ligands; their many coordination sites provide them with remarkable ligation characteristics [17]. The current effort focuses on producing hydrazone ligands from hydralazine using
salicylaldehyde and its metal complexes. The biological activity of the produced complexes is also included in the study.
All chemicals used in this investigation including hydralazine, dibutyltin(IV) dichloride Sn(C4H9)2Cl2, DMSO, and salicylaldehyde were obtained from Sigma Chem. Co. NaOH solution was prepared and standardized against KHphthalate solution. All solutions were prepared in triply distilled water.
Elemental analysis for C, H, and N was carried out on a Perkin-Elmer (2400) CHN analyzer (USA) at the Microanalytical Center of Cairo University, Egypt. 1H spectra were analyzed in DMSO on a Bruker spectrometer (850 MHz) utilizing tetramethylsilane as an internal
reference and 10 mg of the sample. FTIR spectra (KBr) were recorded in a range of 4000–400 cm−1 on a Perkin-Elmer model Frontier spectrometer (USA). TGA was achieved using a Shimadzu TGA-50H thermal analyzer (Japan) provided with standard platinum TG pans. The measurements were carried out in an N2 environment, and the heating rate of 10 °C/min over a temperature range of 25–900 °C was used.
The Schiff-base (L) was prepared by adding an ethanolic solution of 2.01 g (10 mmol) of salicylaldehyde with 10 mmol (1.13 g) of hydralazine hydrochloride in the same volume of ethanol and sodium bicarbonate (3.46 g, 10 mmol). The mixture was then refluxed with continuous stirring for 5 h. The resultant was left overnight, washed with water, ethanol, and diethyl ether several times, and
crystallized from ethanol. The Schiff-base ligand (L) formed yellow crystals, m.p. 190 °C, and yielded 81%. Anal. Calcd.: for C15H12N4O (%); C, 68.71; H, 4.58; N, 21.20. Found (%): C, 69.0; H, 4.7; N, 20.9.
The complex was prepared by refluxing a mixture of (1.3916 g; 5 mmol) of the L, and
Sn(C4H9)2Cl2 (1.0984 g; 5 mmol) in 25 mL of ethanol for 4 h. The solid complex formed was separated and washed with water, ethanol, and diethyl ether. The solid complex was dried in a vacuum desiccator. The color of the formed complex is pale yellow crystals, m.p. 180 °C, and yields 79%. Anal. Calcd.: for C23H29ClN4OSn (%); C, 51.96; H, 5.50; N, 10.54. Found (%): C, 52.0; H, 5.4; N, 10.7.
The absence of water of crystallization was confirmed by TGA. in a N2 atmosphere, for the complex. No loss of weight was observed below 180 °C. The residue is consistent with the formation of Sn metal corresponding to the previously mentioned formulae.
The antimicrobial activities of the ligand and its complex were determined using the agar well diffusion method. The solvent control used is DMSO. The compounds were tested at a concentration of 15 mg/mL against both fungal and bacterial strains.
DFT (density functional theory) calculations have been carried out to investigate the lowest energy geometry of ligand and its complex at the B3LYP/GENECP level of theory, with C, H, N, and O atoms at 6-311G++(dp) and tin atoms at LANL2DZ, using Gaussian 09 proGram [26].
The molecular docking investigations were carried out using MOA2022 software [27]. The structures of ligand and complex were created in PDB file format from the output of Gaussian09 software. The crystal structures of the receptor of Gram +ve bacteria (Staphylococcus aureus) (PDB ID: 1jij) and of the receptor Candida albicans oxidoreductase/oxidoreductase INHIBITOR (PDB ID: 5V5Z) [28] were obtained from the protein data bank (https://www.rcsb.org/).
The prepared [Sn(C4H9)2LCl] complex was inspected by elemental analyses. The results showed a 1:1 complex composition. The mass spectrum of the complex was studied. The molecular ion peak agrees with the suggested formula of the complex, Figure 1. This agrees with elemental analysis results and TGA.

Figure 1: Mass spectrum of L-Schiff base (upper) and complex (lower).
The infrared spectra of L and its complex are shown in Figure 2 and the characteristic IR spectral bands are compared. The absorption at 3730 cm−1 ν(OH) in the free L spectrum is absent in the complex modifying the expression. The stretching vibration at 3310 cm−1 ν(NH) in the IR spectrum of the L is shifted in the spectrum of the complex to 3348 cm−1. The bands at 3043 and 2949 cm−1 in the ligand are due to ν(CH) stretching of aromatic CH and shifted in the complex to 3039 and 2958 cm−1. The bands at 2915 and 2845 cm−1 in the ligand are due to ν(CH) stretching of aliphatic CH and shifted in the complex to 2920 and 2855 cm−1. The stretching vibrations of ν(C⚌N) at 1600 cm−1 in free L are shifted in the complex spectrum to 1606 cm−1. The bending vibrations of δ(NH) at 1525 cm−1 in free L are shifted to 1537 cm−1 in the complex spectrum. The absorption at 586 cm−1 is for ν(Sn─O) in the complex spectrum. The band at 528 cm−1 in the complex spectrum corresponds to the ν(Sn─N) stretching vibration [29,30].
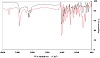
Figure 2: FTIR spectra of L (red) and DBT-L complex (black).
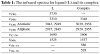
Table 1: The infrared spectra for ligand (L) and its complex.
The 1H NMR spectra of L and its [Sn(C4H9)2LCl] complex were performed in DMSO-d6. The 1H NMR signals (δ, ppm) for free L protons and complex are presented in Figure 3. The 1H NMR spectra of the L ligand exhibited one singlet at 12.10 ppm due to phenolic-OH proton which is absent in the complex spectrum to confirm the involvement of OH-phenolic in the complexation with the ionization of the H atom. The singlet at 10.29 and 10.30 ppm corresponds to the NH proton in the ligand and complex, respectively. The azomethine group N⚌CH singlet is at 8.65 and 8.74 ppm in the ligand and complex, respectively. Also, the 1H NMR spectrum of the L ligand revealed bands between 6.87 and 8.65 ppm corresponding to aromatic protons which shifted to 6.64 to 8.74 ppm in the complex [31,32].

Figure 3: 1H-NMR spectrum of L (above) and its complex (below).
The complex thermogravimetric analysis was carried out in a temperature range from room temperature to 800 °C, Figure 4. The percentage mass loss and thermal effects accompanying the changes in the solid complex on heating are shown in Table 2. The TGA curve shows three steps. The first step shows the loss of a C8H6N3 between 25 and 214 °C, and the second step is due to the loss of C7H5NO between 214 and 370 °C. The third step corresponds to the loss of C4H9Cl between 370 and 565 °C. The last step is due to the loss of C4H9 between 565 and 680 °C. The residue of 22.4% corresponds to Sn, which has a theoretical value of 23.33%.

Figure 4: Thermogravimetric analysis for [Sn(C4H9)2LCl] complex.

Table 2: TGA mass loss of the complex [Sn(C4H9)2LCl] in the temperature range ∼ 25 to 800 °C with 10 degrees/min heating rate.
The molar conductance value of the prepared complex was determined using the relation: ΛM = K/C in 1 × 10−3 M DMSO solution. The value of 31 Ω−1 cm2 mol−1 indicated that the prepared complex is nonelectrolytes. This is because the conductivity values for a nonelectrolyte in a DMSO solution are below 50 Ω−1 cm2 mol−1 [33].
DFT calculations have been carried out to investigate the lowest energy geometry of ligand and its complex at the B3LYP/GENECP level of theory, with C, H, N, and O atoms at 6-311G++(dp) and tin atoms at LANL2DZ, using Gaussian 09 proGram [26]. Figure 5 displays the lowest energy-optimized structure of the ligand. The natural charges obtained from NBO (natural bond orbital) analysis show that the more negative active sites for ligand are O1 (−0.686), N1 (−0.371), N2 (−0.328), N3 (−0.230), and N4 (−0.440). So, the metal ions favor tridentate coordination to O1, N1, and N2, forming 5- and 6-membered chelate rings.
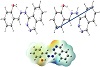
Figure 5: The lowest energy structure, the natural charges on active centers, the vector of the dipole moment, and the MEP (molecular electrostatic potential) surface of ligand.
The optimized structure of the complex [Sn(C4H9)2LCl] as the lowest energy configuration is shown in Figure 6. The tin atom is six-coordinate in a distorted-octahedral geometry and the atoms O1, N1, N2, and Cl7 are almost in one plane deviated by +8.469°, Table 3.
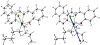
Figure 6: The optimized structure and the natural charges on active centers of [Sn(C4H9)2LCl].

Table 3: Important optimized bond lengths (Å) and bond angles (°) of [Sn(C4H9)2LCl].
The distances between N1••••O1, N1••••N2, and N2••••O1 are decreased from 2.656, 2.944, and 5.532 Å (in free L) to 2.643, 2.647, and 4.178 Å (in the complex), respectively, due to coordination of N1, N2, and O1.
The natural charges computed from the NBO analysis on the coordinated atoms in [Sn(C4H9)2LCl] are Sn (+2.326), O1 (−0.846), N1 (−0.386), N2 (−0.451), C17 (−0.946), C16 (−0.954), and C17 (−0.691).
The computed total energy E, HOMO (the highest occupied molecular orbital) energies, LUMO (the lowest unoccupied molecular orbital) energies, and the dipole moment for the ligands and complexes were calculated, in Table 4. The energy gap (Eg) = ELUMO − EHOMO is smaller in the case of complex than that of ligand due to chelation of ligand to metal ions, Table 7. The lowering of Eg in complexes compared to that of ligands explains the charge-transfer interactions upon complex formation, Figure 7. Reactivity descriptors for example electron affinity (A), ionization potential (I), electronegativity (χ), hardness (η), softness (S), chemical potential (μ), and electrophilicity index (ω), all derived from the HOMO and LUMO energies, have been proposed for understanding various aspects of reactivity associated with chemical reactions, Table 4.
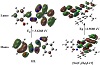
Figure 7: Charge density HOMO and LUMO maps of L and [Sn(C4H9)2LCl].

Table 4: Calculated energies and properties of L and [Sn(C4H9)2LCl].
The ligand and complex structures were generated from the output of Gaussian09 software in PDB file format. The crystal structures of the receptor of Gram +ve bacteria (Staphylococcus aureus) (PDB ID: 1jij) were obtained from the protein data bank (https://www.rcsb.org/).
In the present study, the binding free energy of the ligand and its metal complexes with protein (PDB ID: 1jij) receptor are found to be −4.1, −0.6, and −25.3 kcal/mol for L, (C4H9)2SnCl2, and [Sn(C4H9)2LCl], respectively, Table 5. More negative binding energy means stronger interaction.
Thus, the interaction is in the order of [Sn(C4H9)2LCl] > ligand > (C4H9)2SnCl2.

Table 5: The data calculations of docking interaction for L, (C4H9)2SnCl2, and [Sn(C4H9)2LCl].
The molecular docking studies were achieved with MOA2022 software [27], to find the possible binding modes
of the most active site of the receptor of Staphylococcus aureus (Gram +ve bacteria) (PDB ID: 1jij), Table 5 and Figure 8.
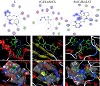
Figure 8: The 2D and 3D graphs of molecular docking studies of the interaction between (A) L, (B) (C4H9)2SnCl2, and (C) [Sn(C4H9)2LCl] with 1jij.
The 2D and 3D plots of the interaction of L, (C4H9)2SnCl2, and [Sn(C4H9)2LCl] with the receptor of Staphylococcus aureus active site are shown in Figure 8.
The molecular docking investigations were carried out using MOA2022 software [27], to find the possible binding ways of the most active site of Candida albicans oxidoreductase/oxidoreductase INHIBITOR (PDB ID: 5V5Z) [28].
The binding free energy of ligand and complex with the receptor of Candida albicans oxidoreductase/oxidoreductase INHIBITOR (PDB ID: PDB ID: 5V5Z) are found to
be −4.6, −1.5, and −119.4 kcal/mol for L, (C4H9)2SnCl2, and [Sn(C4H9)2LCl], respectively, Table 6. The more negative the binding energy, the stronger the interaction. So, the interactions are in the order of [Sn(C4H9)2LCl] > L > (C4H9)2SnCl2.

Table 6: The docking interaction data calculations of L, (C4H9)2SnCl2, and [Sn(C4H9)2LCl] with the active sites of the receptor of Candida albicans oxidoreductase/oxidoreductase INHIBITOR (PDB ID: PDB ID: 5V5Z).
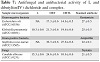
Table 7: Antifungal and antibacterial activity of L and dibutyltin(IV) dichloride and complex.
The 2D and 3D plots of the interaction of L, (C4H9)2SnCl2, and [Sn(C4H9)2LCl] with the active sites of the receptor of Candida albicans oxidoreductase/oxidoreductase INHIBITOR (PDB ID: PDB ID: 5V5Z) are shown in Figure 9.
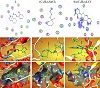
Figure 9: The 2D and 3D graphs of molecular docking studies of the interaction between (A) L, (B) (C4H9)2SnCl2, and (C) [Sn(C4H9)2LCl] with 5V5Z.
The biological activities of a compound depend on the minimum amount by which the chemical substance is vital to inhibit the growth or to kill the microorganism that produces the disease, besides minimum cytotoxicity. Both the ligand and complex were examined for their antifungal and antimicrobial activities. The prepared compounds were examined for their inhibitory effects on the growth of Staphylococcus aureus (Gram-positive) and Escherichia coli (Gram-negative) and Klebsiella pneumonia (Gram-negative), and antifungal Candia albicans at a concentration of 15 mg/mL in DMSO as solvent using Ampicillin is used as standard material Gram-positive Staphylococcus aureus, Gentamicin as standard material Gram-negative Escherichia coli and Klebsiella pneumonia, and Nystatin as standard material Candida albicans since such organisms can attain resistance to antibiotics through biochemical and morphological modification [34].
Antibacterial agents of L, Sn(C4H9)2Cl2, and the complex
are recorded in Table 7 and Figure 10. The antibacterial and antifungal activities were examined by the disc diffusion method. The results indicated the following:
• The results indicated that the L exhibited no activity against Gram-positive Staphylococcus aureus and Gram-negative Escherichia coli but moderate activity against Klebsiella pneumonia and Candida albicans.
• The data indicated that the complex has lower activity against the fungal strains when compared to standard Nystatin.
• The results indicated that the complex exhibited higher activity against Gram-positive Staphylococcus aureus than Gram-negative Escherichia coli and Klebsiella pneumonia as a broad-spectrum antibiotic and highly promising for MRSA (methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus) and multi-drug resistant (MDR).

Figure 10: Antibacterial and antifungal activity of L, (C4H9)2SnCl2, and the complex at 15 mg ml−1 concentration of Gentamicin, Ampicillin, and Nystatinas standard as references of antifungal and antibacterial agents for Gram-negative and Gram-positive bacteria and Candida albicans, respectively.
The condensation reactions of the organotin(IV) complex form an octahedral complex of Sn(IV) produced by the reaction of dibutyltin(IV) dichloride with Schiff bases of hydrazone ligands. The molecular properties of the complex and ligand as hardness, the HOMO-LUMO gap, bond angles, and bond lengths have been investigated employing DFT calculations. The results show that the complex has higher activity against Gram-positive Staphylococcus aureus than Gram-negative Escherichia coli and Klebsiella pneumonia. The use of the complex in drug design could have a substantial influence on human lives and give different medication which might be cheaper and better than the currently available drugs. The prepared complex can act as a broad-spectrum antibiotic and is highly promising for MRSA and MDR.
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
- N. Muhammad, A. Shah, Z. Rehman, et al., Organotin(IV) 4-nitrophenylethanoates: Synthesis, structural characteristics and intercalative mode of interaction with DNA, J Organomet Chem, 694 (2009), 3431–3437.
- A. S. Al Alousi, M. R. Shehata, M. M. Shoukry, and N. M. Mohamed, Interaction of dimethyltin(IV) and trimethyltin(IV) with dehydroacetic acid, Chem Speciat Bioavailab, 21 (2009), 1–6.
- A. A. Al-Najjar, M. M. Mohamed, M. R. Shehata, and M. M. Shoukry, Tripropyltin(IV) complexes with some selected bioligands in 50% V/V dioxane/water mixture, Ann Chim, 96 (2006), 97–107.
- A. Abdel Wahab, M. Shoukry, M. R. Shehata, and P. Khalf-Alla, Synthesis, equilibria, DFT and biological investigation of
homopiperazine complex with diphenyltin(IV), Egypt J Chem, 65 (2022), 687–699.
- A. A. El-Sherif, M. R. Shehata, M. M. Shoukry, and N. M. Mahmoud, Potentiometric study of speciation and thermodynamics of complex formation equilibria of diorganotin(IV) dichloride with 1-(2-aminoethyl)piperazine, J Solution Chem, 45 (2016), 410–430.
- M. M. Shoukry, M. R. Shehata, and A. M. Abdel Wahab, Synthesis, characterization, thermal degradation, docking, DFT calculation, and biological activity of dimethyltin(IV) complex with homopiperazine, J Chin Chem Soc, 68 (2021), 2164–2176.
- M. R. Shehata, M. M. Shoukry, and A. M. Abdel Wahab, Equilibrium studies of binary and mixed-ligand dimethyltin(IV) complexes involving homopiperazine and DNA constituents with reference to the antitumor activity, Phys Chem Liquids, 59 (2021), 523–536.
- A. A. El-Sherif, M. R. Shehata, M. M. Shoukry, and N. M. Mahmoud, Equilibrium studies of diethyltin(IV) dichloride and divinyltin(IV) dichloride with 1-(2-aminoethyl)-pyrrolidine, J Mol Liq, 262 (2018), 422–434.
- M. M. A. Mohamed, M. R. Shehata, and M. M. Shoukry, Trimethyltin(IV) complexes with some selected DNA constituents, J Coord Chem, 53 (2001), 125–142.
- A. Al-Najjar, M. R. Shehata, M. M. A. Mohamed, and M. M. Shoukry, Equilibrium studies of organotin(IV) complexes of peptides, Main Group Metal Chemistry, 22 (1999), 253–262.
- M. R. Shehata, M. M. A. Mohamed, M. M. Shoukry, M. A. Hussein, and F. M. Hussein, Synthesis, characterization, equilibria and biological activity of dimethyltin(IV) complex with 1,4-piperazine, J Coord Chem, 68 (2015), 1101–1114.
- O. Al-Flaijj, M. R. Shehata, M. M. A. Mohamed, and M. M. Shoukry, Interaction of dimethyltin(IV) with DNA constituents, Monatsh Chem, 132 (2001), 349–366.
- P. A. Khalaf-Alla, M. M. Shoukry, M. R. Shehata, A. M. Abdel Wahab, and R. Van Eldik, Synthesis, equilibrium, DFT, and docking studies of a homopiperazine complex with dibutyltin(IV), J Coord Chem, 77 (2024), 880–895.
- J. Ceramella, D. Iacopetta, A. Catalano, F. Cirillo, R. Lappano, and M. S. Sinicropi, A review on the antimicrobial activity of Schiff bases: Data collection and recent studies, Antibiotics, 11 (2022), 191.
- C. M. da Silva, D. L. da Silva, L. V. Modolo, et al., Schiff bases: A short review of their antimicrobial activities, J Adv Res, 2 (2011), 1–8.
- K. Rana, A. Pandurangan, N. Singh, and A. K. Tiwari, A systemic review of Schiff bases as an analgesic, anti-inflammatory, Int J Curr Pharm Res, 4 (2012), 5–11.
- P. K. Singh and D. N. Kumar, Spectral studies on cobalt(II), nickel(II) and copper(II) complexes of naphthaldehyde substituted aroylhydrazones, Spectrochim Acta A Mol Biomol Spectrosc, 64 (2006), 853–858.
- A. D. Garnovskii, A. L. Nivorozhkin, and V. I. Minkin, Ligand environment and the structure of Schiff base adducts and tetracoordinated metal-chelates, Coord Chem Rev, 126 (1993), 1–69.
- M. J. M. Campbell, Transition metal complexes of thiosemicarbazide and thiosemicarbazones, Coord Chem Rev, 15 (1975), 279–319.
- D. R. Williams, Metals, ligands, and cancer, Chem Rev, 72 (1972), 203–213.
- H. Naeimi, J. Safari, and A. Heidarnezhad, Synthesis of Schiff base ligands derived from condensation of salicylaldehyde derivatives and synthetic diamine, Dyes and Pigments, 73 (2007), 251–253.
- P. Panneerselvam, B. A. Rather, D. Ravi Sankar Reddy, and N. Ramesh Kumar, Synthesis and anti-microbial screening of some Schiff bases of 3-amino-6,8-dibromo-2-phenylquinazolin-4(3H)-ones, Eur J Med Chem, 44 (2009), 2328–2333.
- S. N. Pandeya, D. Sriram, G. Nath, and E. DeClercq, Synthesis, antibacterial, antifungal and anti-HIV activities of Schiff and Mannich bases derived from isatin derivatives and n-[4-(4′-chlorophenyl)thiazol-2-yl] thiosemicarbazide, Eur J Pharm Sci, 9 (1999), 25–31.
- M. S. Karthikeyan, D. J. Prasad, B. Poojary, K. Subrahmanya Bhat, B. S. Holla, and N. S. Kumari, Synthesis and biological activity of Schiff and Mannich bases bearing 2,4-dichloro-5-fluorophenyl moiety, Bioorg Med Chem, 14 (2006), 7482–7489.
- M. Pervaiz, A. Munir, A. Riaz, et al., Amalgamation, scrutinizing, and biological evaluation of the antimicrobial aptitude of thiosemicarbazide Schiff bases derivatives metal complexes, Inorg Chem Commun, 141 (2022), 109459.
- M. J. Frisch, G. W. Trucks, H. B. Schlegel, et al., Gaussian 09, Revision A.02, 2016.
- Molecular Operating Environment (MOE), 2022.02 Chemical Computing Group ULC, 910-1010 Sherbrooke St. W., Montreal, QC H3A 2R7, https://www.chemcomp.com/en/Research-Citing_MOE.htm, 2022.
- M. V. Keniya, M. Sabherwal, R. K. Wilson, et al., Crystal structures of full-length lanosterol 14α-demethylases of prominent fungal pathogens Candida albicans and Candida glabrata
provide tools for antifungal discovery, Antimicrob Agents Chemother, 62 (2018), e01134–18.
- K. Nakamoto, Infrared and Raman Spectra of Inorganic and Coordination Compounds: Part B: Applications in Coordination, Organometallic, and Bioinorganic Chemistry, John Wiley & Sons, Hoboken, NJ, 2009.
- W.-J. Jiang, Y.-J. Tan, J.-T. Man, and Y.-X. Tan, Syntheses, crystal structures, anticancer activities and DNA-binding properties of the dibutyltin complexes based on benzoin aroyl hydrazone, Chin J Struct Chem, 41 (2022), 2202105–2202113.
- A. A. El-Sherif and T. M. Eldebss, Synthesis, spectral characterization, solution equilibria, in vitro antibacterial and cytotoxic activities of Cu(II), Ni(II), Mn(II), Co(II) and Zn(II) complexes with Schiff base derived from 5-bromosalicylaldehyde and 2-aminomethylthiophene, Spectrochim Acta A Mol Biomol Spectrosc, 79 (2011), 1803–1814.
- A. J. Crowe, Tin compounds and their potential as pharmaceutical agents, in Tin-Based Antitumour Drugs, M. Gielen, ed., Springer, Berlin, 1990, 69–114.
- O. I. Alajrawy, H. A. Hadi, R. S. A. Al-Luhaibi, and B. A. Sabbar, In-vitro cytotoxic activity and theoretical investigations for new mononuclear Pt(IV) and dinuclear Ru(III) with o-phenylenediamine ligand complexes against L20B cell line, Results Chem, 5 (2023), 100712.
- A. C. Scott, Laboratory control of antimicrobial therapy, in Mackie & McCartney—Practical Medical Microbiology, J. G. Collee, J. P. Duguid, A. G. Fraser, and B. P. Marmion, eds., Churchill Livingstone, Edinburgh, 13th ed., 1989, 161–181.
Copyright © 2025 Abeer Taha Ibrahim et al. This is an open access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License, which permits unrestricted use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided the original work is properly cited.